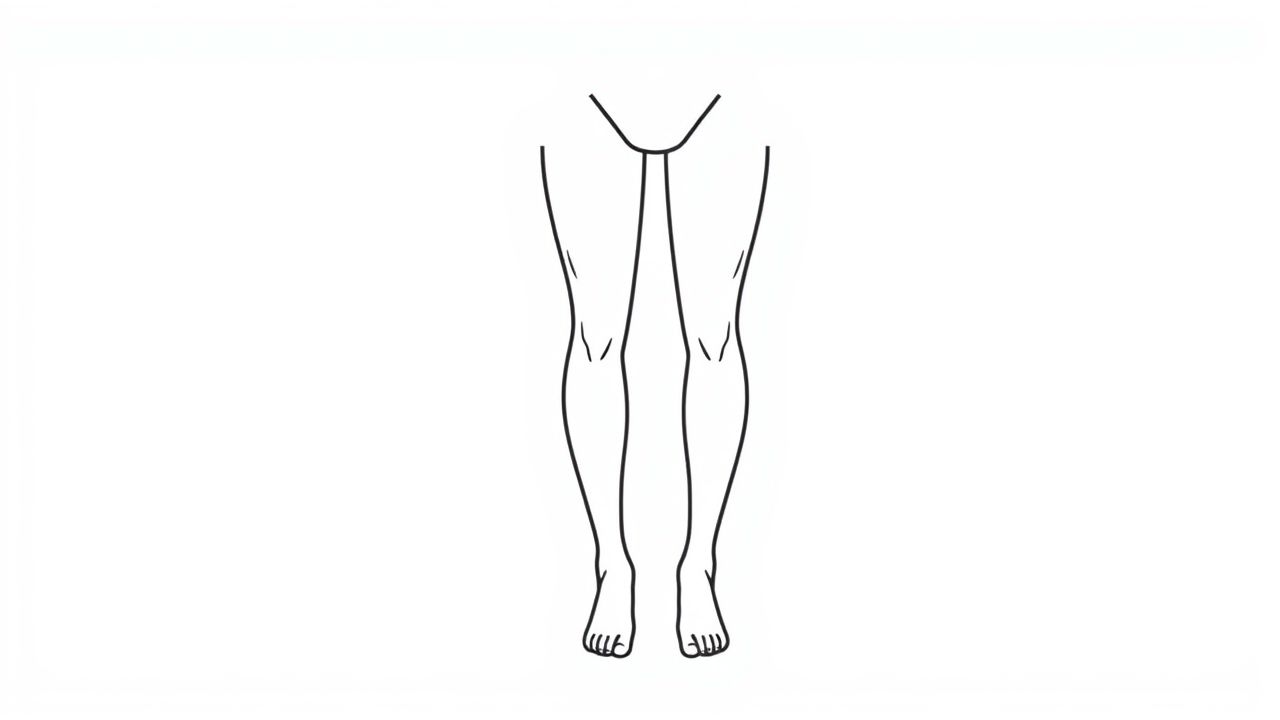
Bow legs, medically known as genu varum, is a condition in which the legs curve outward at the knees while the feet and ankles touch. This creates a noticeable gap between the knees when a person stands with their feet together. While bow legs can be a normal part of development in infants and toddlers, persistent or severe curvature in older children and adults may indicate an underlying medical problem that needs evaluation. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of bow legs can help people manage the condition effectively and prevent complications in the future.
Understanding Genu Varum
Genu varum describes an outward bowing of the legs in relation to the thighs. In newborns and toddlers, the condition is common because the legs have been curled in the womb. As children grow and start walking, the alignment typically straightens by the age of 3. However, if the curvature continues beyond early childhood, it may be linked to conditions such as rickets, bone dysplasia, or Blount’s disease.
Normal Development vs. Persistent Bow Legs
It is important to distinguish between normal developmental bow legs and pathological genu varum. In normal cases, the curvature is mild, symmetrical, and gradually improves with age. In persistent cases, the curvature may worsen, be uneven, or cause discomfort, requiring medical assessment.
Causes of Bow Legs
Several factors can lead to genu varum. The causes can be categorized into developmental, pathological, and acquired conditions.
- Physiological bow legsCommon in infants and toddlers, usually resolves on its own by age 3.
- RicketsA condition caused by vitamin D deficiency leading to soft and weak bones.
- Blount’s diseaseA growth disorder of the shin bone (tibia) causing progressive bowing.
- Bone dysplasiaGenetic disorders affecting bone growth and shape.
- Fractures and injuriesImproper healing of bone injuries can cause misalignment.
- ArthritisJoint degeneration can alter leg alignment in adults.
Signs and Symptoms
The most noticeable symptom of genu varum is the gap between the knees when standing with feet together. Other possible symptoms include
- Knee pain or discomfort
- Uneven walking pattern or limp
- Hip or ankle pain due to altered biomechanics
- Visible curvature of one or both legs
- Unequal leg lengths in severe cases
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of bow legs involves a physical examination and medical history review. The doctor may assess leg alignment, gait, and any associated pain. In persistent or severe cases, imaging tests such as X-rays can help determine the underlying cause and measure the degree of curvature.
Key Diagnostic Steps
- Measuring the gap between knees
- Checking for asymmetry between legs
- Evaluating hip, knee, and ankle movement
- Blood tests for vitamin D levels if rickets is suspected
Treatment Options
Treatment for genu varum depends on the underlying cause, age of the patient, and severity of the curvature.
For Children
- ObservationMany mild cases improve naturally without treatment.
- Nutritional supportVitamin D and calcium supplements in cases of deficiency.
- BracingCorrective braces for children with Blount’s disease or progressive curvature.
For Adults
- Physical therapyStrengthening and stretching exercises to improve leg alignment and reduce discomfort.
- MedicationsPain relief for arthritis-related bow legs.
- SurgeryProcedures such as osteotomy to realign the bones in severe cases.
Complications if Left Untreated
Ignoring persistent bow legs can lead to several long-term complications, including
- Chronic knee or hip pain
- Increased risk of osteoarthritis
- Difficulty walking or running efficiently
- Progressive joint damage due to uneven weight distribution
Prevention and Lifestyle Tips
While not all cases of genu varum can be prevented, certain measures can help maintain healthy leg development and bone strength.
- Ensuring adequate vitamin D and calcium intake
- Encouraging outdoor activities for natural sunlight exposure
- Early detection and treatment of bone or joint problems
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce strain on joints
Living with Bow Legs
For individuals with mild bow legs that do not cause pain or functional issues, the condition may not significantly impact daily life. However, for those with discomfort or mobility challenges, physical therapy, supportive footwear, and regular medical check-ups can improve quality of life.
Psychological and Social Considerations
Children and adults with visible leg curvature may experience self-consciousness or teasing. Providing education, support, and reassurance can help boost confidence and promote a positive self-image.
When to See a Doctor
Medical evaluation is important if bow legs are accompanied by pain, worsen over time, are asymmetrical, or persist beyond early childhood. Early diagnosis allows for timely treatment, which can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Bow legs, or genu varum, can range from a normal developmental phase to a sign of an underlying health condition. While many cases in young children resolve naturally, persistent curvature requires medical attention. With proper diagnosis, treatment, and supportive care, individuals with bow legs can maintain good mobility, reduce discomfort, and enjoy a healthy, active lifestyle.